Welcome, Setup, Github Accounts
Welcome! This week we will talk about what we plan to do over the course of the next few weeks and some logistics.
tl;dr of this program
You will learn how use Github, and you will learn how to make your own website.
What are we doing today?
- Introductions
- What is Triton Software Engineering?
- Why are you here?
- Google is your friend.
- What is Git?
- What is Github?
- What is Github Desktop?
- Task: Make your own github accounts!
Introductions:
Wesley Chen
Hi! My name is Wesley Chen, and I am a Junior majoring in Computer Engineering at UCSD. I am also minoring in Music.
Interests:
- Computer
- Music
- Swimming
- Sleep
- Community Service
Why you should believe what I say:
- I was also still in high school two years ago
Benson Budiman
Hey! My name is Benson Budiman, and I am a Junior majoring in Computer Science at UCSD.
My interests are the same as Wesley’s (except I don’t swim), and I was also still in high school two years ago.
What is Triton Software Engineering?
Triton Software Engineering (TSE) is a multidisciplinary student organization at UC San Diego. We partner with nonprofits to design and develop software (e.g. websites or mobile applications) pro-bono for social good while giving our students practical, real-world experience.
Our founding members established TSE in the Spring of 2017. They saw that nonprofit organizations had very few resources to procure professional web and technical development services, and that for these nonprofits, such antiquated processes and tools led to significant organizational breakdowns. This is where TSE steps in. By providing a venue for both student developers and nonprofit organizations to connect, we foster growth in both social good and technical expertise.
We believe that technology should be accessible to the community and especially to those who serve the community; something as simple as a sleek, updated, and easy-to-use website or as complicated as a mobile app to track donations can have immediate impact and value for any organizations of any size.
Let us help you help the community.
Check us out here!
Why are you here?
The goal of this program is to give you some insight into what it is like to be a software developer. Maybe you will be inspired and become a CTO (Chief Techincal Officer) of some company worth billions of dollars (and if so, please hook me up with a job).
In this program, you will learn how to make your very own website, which you can put on your college resume.
Having any web development skills is quite important these days as our society transitions to heavily rely on the internet. Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter are web services that you probably use on a daily basis - people who learned web development went to made those for the community!
Google is your friend.
Before we get started with our program, we should remind you about the importance of Google.
You probably used Google when you had any questions about anything or if you were stuck on your homework. Likewise, any good developer should know how and when to use Google. If you have a problem, then you should ask the internet first. Most of the time, the resources found can be used to your advantage. Therefore, if you don’t know, then ask Google!
Git
If you are a programmer, you should know what Git is.
— Wesley Chen, 2019
You might have used Google Drive or DropBox to store and view documents on the cloud. However, software developers use Git and GitHub to store and view their code on the cloud.
If you are unfamiliar with Git and GitHub, This handbook is pretty good at explaining what Git is. It also serves as a nice refresher if you do know Git already. Read it thoroughly, and then we’ll summarize the essentials here.
Basically, Git is a system that keeps a history of any changes to files - it can help you determine exactly what files changed, when they were changed, who changed them, and the reasons why they were changed.
Git is extremely useful when keeping track of collaborative work. For example: when multiple people are working on a project, the collaborators can report their progress by creating their own personal branch to make any update or changes (e.g. adding extra lines of code to a file or adding a new picture inside a folder), taking a “snapshot” of their changes, then asking to have this “snapshot” of their changes added to the main branch.
There are a bunch of uses for Git, such as:
- Viewing the history of the entire project
- Adding or modifying files
- Creating your own branch to work on
- Merging your own branch into the main branch
Below are some examples of basic commands:
Create your own project repository from scratch.
git init [folder_name]
A repository named [folder_name] will be created and will become your working directory (i.e. folder that holds your project)! Now, any changes you make can be committed into its history.
Clone an existing project repository from somewhere online.
git clone [git_link]
This will download the latest “snapshot” from that online repository and become a working directory for you.
View the status of your current working directory.
git status
This will print some basic information, including the files you have changed, and any changes ready to be “snapshotted” into history.
There are a bunch of stuff to understand about Git (which can be learned through the handbook above), but the basic flow of using Git in a personal project goes something like this:
- You make any changes you want to your working directory (whether you checked-out a branch or not - just anywhere in the project directory).
- Once you are satisfied with those changes, you can stage them to the staging area. In other words, this is where you take those “snapshots” of the changes then add it to an temporary “changes” area before you actually add it to your history of changes. To stage everything in your working directory, you would type the following in the terminal:
git add *. - Once you are satisfied with all “snapshots” in your staging area, you can commit them, which takes these “snapshots” and permanently stores them to your local Git directory. In other words, your changes are now part of the project history and in the future, you can always check what changes you have made at this point. To commit everything in your staging area, you would type the following in the terminal:
git commit -m [message]. Inside[message], you can type why you decided to make these changes (honestly just type anything).
Here is a picture of the Git workflow:
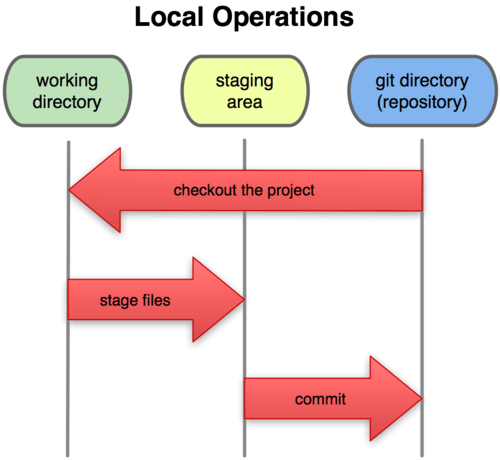
If you still are confused (even after reading the handbook), don’t forget that Google is your friend - feel free to search up anything you need help with!
Github
Github is a website that helps us developers store and manage our code. Google search results can give us more insight into what Github is. Some features that Github provide for developers make it really easy for us to do pretty cool things, like using Git commands without knowing any command line interface or have our own website hosted online for free!
Github Desktop
In the next lesson, we will explore what Github Desktop is and how we will use it to our advantage. Github Desktop is an application that allows us to use Git commands without needing any command line interface.
Task: Make a Github account!
One of the first steps of succeeding in this program is by making a Github account.
Steps:
- Go to github.com.
- Click “Sign up” to create an account. Alternatively, “Sign in” if you already have an account.
- If you are creating a new account, think carefully about your username! If you want to show off your work, then colleges and workplaces will see your GitHub username attached to it. This means while _xxxBigBallerMoneySwagMasterxxx_ is a cool username, it probably will not reflect very well in front of the college admissions staff or to any recruiter. A suggestion for your username is to make it a shortened version of your full name. Fortunately, anyone can change their username afterwards in your settings.
- Follow the instructions of this guide to make your own repository!
- Congratulations! You’re one step closer to succeeding in this program and becoming a developer!